trichomes are external secretory structures, which are present in about 30% of plant species. For instance, the smell of plants is mostly because of the volatile substances released by these structures. Glandular trichomes are commonly multicellular, with glandular cells at the distal end attached to the epidermis by non-glandular cells known as basal cells and by other forming a stalk or peduncle. However, some thrichomes are unicellular. Glandular cells have a primary cell wall, sometimes covered by a cuticle at the joining area with the stalk cells, and contain a cytoplasm with abundant organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi cistern stacks. However, there are differences between glandular cells of different species. For example, glandular cells releasing terpenes contain very scarce Golgi apparatus or it is not visible at all.
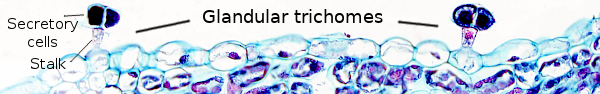
Glandular trichomes contain cells that release substances with different functions to the environment, either volatile or substances that remain on the surface of the plant. Glandular cells can synthesize the molecules to be released, even they have sometimes the ability to perform photosynthesis. It means that some glandular cells may live as rather independent units. However, in other cases the molecular building blocks for synthesizing the compounds to be release are coming from the underlying plant tissues through the stalk cells of the trichome.
Glandular trichomes are classified according to the compounds they release or the trichome morphology. There are thichomes with a basal cell, one or more in the stalk, and a few secretory cells at the distal end. These trichomes commonly release not very volatile substances that are laid on the surface of the plant. Other types of trichomes show a basal cell, a short cell in the stalk, and a head with one or several secretory cells showing a large cavity between the cuticle and the primary cell wall, which is filled with substances. There are many other examples of glandular trichomes. It can be found different types of trichomes in the same plant, even in the same organ. For example, in carnivorous plants, there are trichomes for fetching the insect by releasing mucilaginous substances or nectar, and others release proteolitic enzymes for digestion. The amount of trichomes, both glandular and not glandular, is influenced by the environment. For instance, it can be increased after the attack of a herbivore.
RELATED POSTS
View all
